normal end tidal co2 after intubation
2 See Figure 1 p. Capnography is also the most reliable indicator that an endotracheal tube is placed in the trachea after intubation.
Abnormal Capnography Waveforms And Their Interpretation Deranged Physiology
2 to near normal normal EtCO 2 35-45 mmHg represents marked increase of CO 2 delivery to lungs suggesting ROSC If patient develops an organized rhythm after VFVTasystole check EtCO 2 to see if ROSC has occurred CONFIRM PLACEMENT OF ETT After intubation if ETCO 2 10mm Hg tube in trachea.

. 48 When a person is breathing out CO 2 the graph goes up. MmHg Relate to the air we breath. A semiquantitative colorimetric FEF end-tidal CO2 detector Fenem Inc.
Total pressure of a gas is the sum of the partial pressures of the gas Expired CO2 measured PetCO2 mmHg in waveform Percentage Normal Levels PaO2 85-100mmHg PaCO2 35-45mmHg Percentage vs. In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign. End tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 monitoring is the noninvasive measurement of exhaled CO 2 first studied clinically by Smallhout and Kalenda in the 1970s.
1 ACLS guidelines define high quality chest compressions as. When a person is breathing in it. The normal values of end-tidal CO 2 is around 5 or 35-37 mm Hg.
End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 monitoring and capnography have become an integral part of the daily management of critically ill patientsBy monitoring ETCO 2 providers acquire information on a patients pulmonary cardiac and metabolic status. The gradient between the blood CO 2 PaCO 2 and exhaled CO 2 end-tidal CO 2 or PetCO 2 is usually 5-6 mm Hg. Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status.
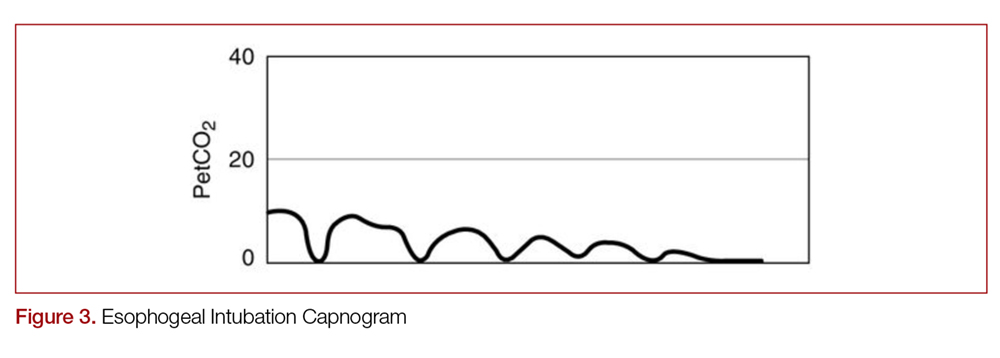
Two very practical uses of waveform capnography in CPR are. This will cause a decrease in the ETCO2 end-tidal CO2 and this will be observable on the waveform as well as with the numerical measurement. End-tidal CO2 measurement in the detection of esophageal intubation during cardiac arrest.
Finally the endotracheal tube was found to be in the esophagus at postmortem. The second intubation showed a normal end-tidal carbon dioxide wave form that declined over a minute accompanied by decreasing oxygen saturation. In this study the aim was to review the applications of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 monitoring in emergency department multiple databases were comprehensively searched with combination of following keywords.
2345 ETCO 2 monitoring is one of the objective. 11172009 4 Measuring End Tidal CO2 Daltons Law. Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition.
ETCO2 emergency department monitoring and critical. Measurement of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 has been used to detect accidental esophageal tube placement in noncardiac arrest situations. Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient should be 35-45 mmHg.
A prospective clinical trial was conducted at a level I trauma center to assess the efficacy of end-tidal carbon dioxide CO2 detection in four groups of patients requiring emergency intubation because of cardiac arrest major trauma respiratory failure or the need for airway protection. In hyperventilation the CO2 waveform becomes smaller and more frequent and the numeric reading falls below the normal range. An increase in etCO2 by 5 appears to have reasonable sensitivity 71-91 and specificity 94-100 for fluid responsiveness in two studies of patients breathing passively on the ventilator.
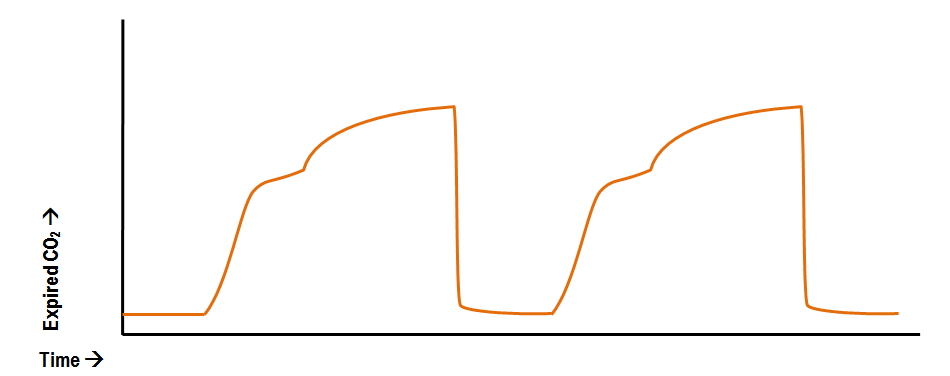
428 153 mmHg versus 323 141 mmHg. Capnography is the most reliable indicator that an endotracheal tube is placed in the trachea after intubation. The normal end-tidal capnography wave form is basically a rounded rectangle.
End-tidal CO2 may be useful here as an easily and immediately measurable index of changes in cardiac output. 1 evaluating the effectiveness of chest compressions and 2 identification of ROSC. On average during CPR if adequate chest compressions are being delivered a cardiac index of 16-19 Lminm2 can be generated which correlates with ETCO2 pressures of 20mmHg.
Riley and Marcy presented a case report where they were able to diagnose endobronchial intubation when there was a rise in end-tidal CO2 from 41 to 613 The rise in end-tidal PCO2 was the result of reduced ventilation consequent to leakage of tidal volumes around a non-cuffed tube migrating into the bronchus thereby increasing the. In the awake adult normal cardiac index lies between 25-4 Lminm2 with an ETCO2 of 35-45 mmHg. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation.
A normal trace appears as a series of rectangular waves in sequence with a numeric reading capnometry that shows the value of exhaled CO2. Mainstream end tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 is one of the methods used for this purpose during general anaesthesia of intubated patients in the operating theatre. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG.
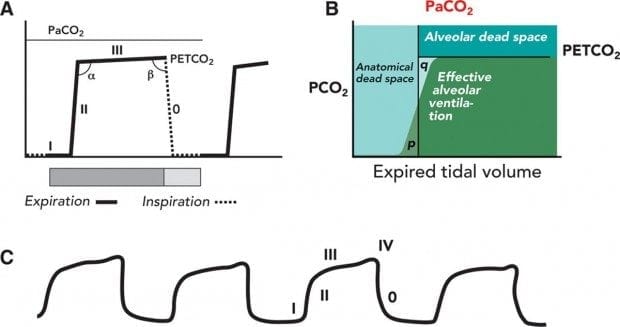
Changes in the shape of the capnogram are diagnostic of disease conditions while changes in end-tidal CO 2 EtCO 2 the maximum CO 2 concentration at the end of each tidal breath can be used to assess disease severity and response to treatment. 78 Nitrogen 21 Oxygen 1 CO2 and other gases Exhaled gases. The purpose of our study was to determine whether ETCO2 measurement could distinguish tracheal from esophageal tube.
By 1978 the technology was finally adopted in Holland. 1 It has been used extensively in operating theatres and intensive care units for the past 25 years and increasingly in emergency departments and the prehospital setting. Capnograph is an indispensable tool for monitoring metabolic and respiratory function.
Authors A J Sayah 1 W F Peacock D. The first infrared monitoring and recording device was created in 1943. Normal ETCO2 is in the range of 35 to 45 mmHg.
PetCO 2 can be used to estimate PaCO 2 in patients with essentially normal. End tidal CO 2 monitoring is represented as a number and a graph on a monitor.

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

A Systematic Approach To Capnography Waveforms Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News
End Tidal Capnography In The Emergency Department Mdedge Emergency Medicine

Pin On Do What You Love Love What You Do

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Image Result For Capnography Ventilator Cheat Sheets Cheating Things To Come

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall
Capnography Waveform Interpretation Litfl Ccc Equipment

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

